Building A Simple Proxy Server With Raspberry Pi
About the project
Discover the simplicity of setting up a proxy server on your Raspberry Pi using the user-friendly and open-source software known as Squid.
Project info
Difficulty: Easy
Platforms: Raspberry Pi
Estimated time: 1 hour
License: GNU Lesser General Public License version 3 or later (LGPL3+)
Items used in this project
Story
Discover the simplicity of setting up a proxy server on your Raspberry Pi using the user-friendly and open-source software known as Squid. In this tutorial, we provide a step-by-step guide, demonstrating its application for web scraping. However, the advantages of establishing a proxy server extend beyond this, encompassing enhanced security, efficient caching, accelerated networking requests, and streamlined connection management. Unlock the potential of your Raspberry Pi with this comprehensive tutorial on Squid proxy server setup!
Before reading the remainder, be sure to subscribe and support the channel if you have not!
Subscribe:
Support:
https://www.buymeacoffee.com/mmshilleh
Hire me at UpWork to build your IoT projects:
https://www.upwork.com/freelancers/~017060e77e9d8a1157
Part 1: Setting up the Raspberry PiInitial Setup:- Ensure your Raspberry Pi 4 is set up with Raspbian (or another compatible OS) and that it's connected to the internet.- Access your Raspberry Pi terminal through SSH or directly using a monitor and keyboard.
Update and Upgrade Packages:- Run sudo apt-get update and sudo apt-get upgrade to ensure all packages are up to date.
Install Squid:- Execute sudo apt-get install squid.- Once installed, the Squid service should start automatically.
Configure Squid:- Backup the original configuration file: sudo cp /etc/squid/squid.conf /etc/squid/squid.conf.backup.- Edit the configuration file: sudo nano /etc/squid/squid.conf.
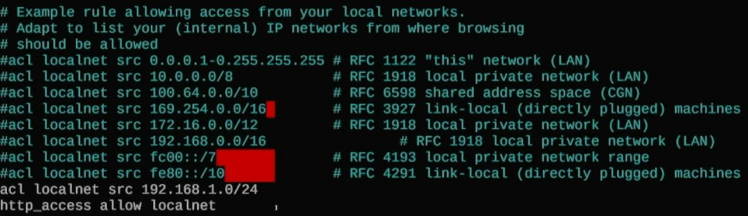
You can see the lines are uncommented:
acl localnet src 192.168.1.0/24
http_access allow localnet
This is needed to only allow devices on your local home network to connect to the proxy. It is a very simple setting; you can play with the config in this file to filter what IPs and what network security parameters you would like to configure. For the sake of this video, we keep it simple.
Restart Squid:Restart the Squid service to apply the changes: sudo systemctl restart squid.
Verify Squid is Running:Check the status of Squid: sudo systemctl status squid.
Get Raspberry Pi IP Address:
To get the Raspberry Pi IP address you can type in the command ifconfig in the terminal and look at the inet address. You will need this address to use on the Python script on your local computer that will send the scraping request to the Pi's IP address first as proxy!
Part 2: Local Computer CodeCreate a Python Script on your local computer and run the following script, make sure you substitute your Pi IP address.
https://github.com/shillehbean/youtube-p2/blob/main/test_proxy.py
This script is designed to scrape web content from a specified URL (in this case, a search page on eBay for laptops) using the Python requests library for making HTTP requests and the BeautifulSoup library from bs4 for parsing HTML content. The script uses a proxy server to make the request. Here's a step-by-step explanation:
- Import Libraries:
import requests: Imports therequestslibrary, which is used to send HTTP requests easily in Python.from bs4 import BeautifulSoup: Imports theBeautifulSoupclass from thebs4(Beautiful Soup) library. Beautiful Soup is used for parsing HTML and XML documents, making it easier to navigate, search, and modify the parse tree. - Set Up Proxies:The
proxiesdictionary is defined with keys'http'and'https', each containing the URL of the proxy server (http://192.168.1.111:3128). This tells therequestslibrary to route HTTP and HTTPS requests through the proxy server at the specified IP address (192.168.1.111) and port (3128). - Specify Target URL:The
urlvariable is set to the target URL, which in this case is an eBay search page for laptops. - Send HTTP GET Request:
response = requests.get(url, proxies=proxies): Sends an HTTP GET request to the specifiedurl. Theproxiesparameter is used, meaning the request will be sent through the proxy server defined earlier. - Check Response Status:The script checks if the HTTP request was successful by examining
response.status_code.HTTP status code 200 indicates success. If the request was successful (response.status_code == 200), the script proceeds to parse the response content. - Parse and Print HTML Content (if successful):
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.content, 'html.parser'): Parses the content of the HTTP response (response.content) using Beautiful Soup, which creates a BeautifulSoup object (soup). The'html.parser'argument specifies the parser to use.print(soup): Prints the parsed HTML content to the console. In a more practical scraping scenario, you would use Beautiful Soup's functionality to extract specific data fromsoup(like product names, prices, etc.) instead of printing the entire HTML content. - Handle Failed Request (if not successful):If the HTTP request was not successful (status code is not 200), the script prints a message indicating that the webpage retrieval failed, along with the HTTP status code received.
In a real-world scenario, you'd likely want to add more functionality after parsing the HTML to extract and process the specific data you're interested in.
Conclusion:Hope you enjoyed the quick tutorial, if the Python script ran it means that the requests are going through your Pi's IP address which can help you webscrape, let me know if you have any questions.
If you enjoy the video, please subscribe to my channel Shilleh on Youtube in the video above, your support would be appreciated. Ping me for any questions, thanks everyone!
Credits

mahmood-m-shilleh
Mechanical and Software Engineering Background. University at Buffalo 2019 Texas A&M 2021 I make data pipelines for my day job. Outside of work, I participate in online communities regarding Full Stack Engineering, Microelectronics, and more. You can find more details about me on my Youtube Channel. https://www.youtube.com/@mmshilleh Feel free to reach out!