Arduino And Visuino: Control Smart Car Robot With Joystick
About the project
Smart Car sets, when combined with L298N Motor Driver Modules, offer one of the easiest ways to make robot cars.
Project info
Difficulty: Easy
Estimated time: 1 hour
License: GNU General Public License, version 3 or later (GPL3+)
Items used in this project
Hardware components
Software apps and online services
Story
Smart Car sets, when combined with L298N Motor Driver Modules, offer one of the easiest ways to make robot cars. The L298N Motor Driver Module is easy to control with Arduino, and with the help of Visuino you can program your car in seconds.
In this Tutorial I will show you how easy it is to control a Smart Car with an analog Joystick. In the following tutorials I will show you more interesting and complex robot designs, so stay tuned.
Step 1: Components
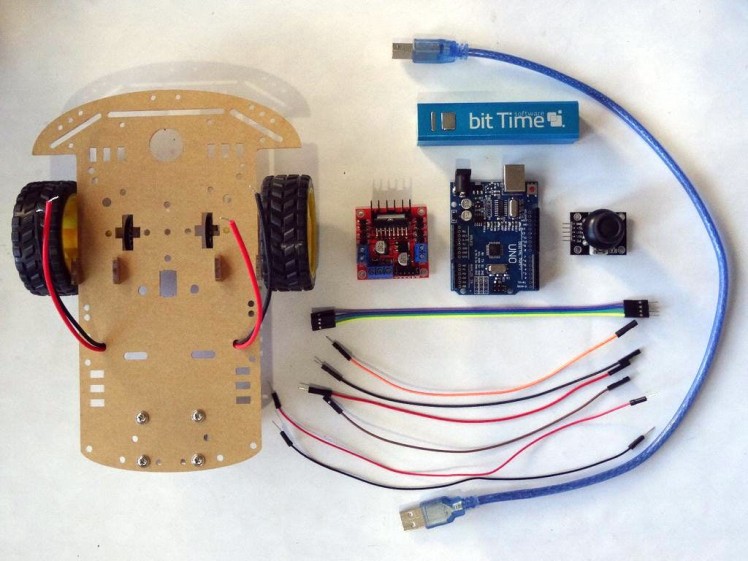
- One Smart Car chassis with 2 DC motors, gears and wheels
- One Arduino board (I used Arduino UNO, but any other will be just fine)
- One L298N Dual Motor Driver Module
- One Joystick that I got from this cheap 37 sensors set
- One USB Power supply with USB Cable (I used a USB Power Bank but any other option will work)
- 2 Male-Male jumper wires
- 8 Female-Male jumper wires
1 / 3 • Picture 1

Picture 1
Picture 2
Picture 3
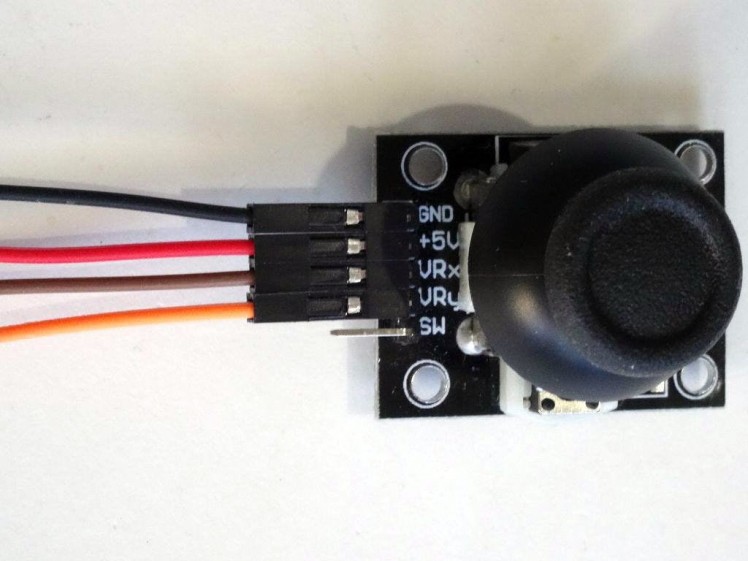
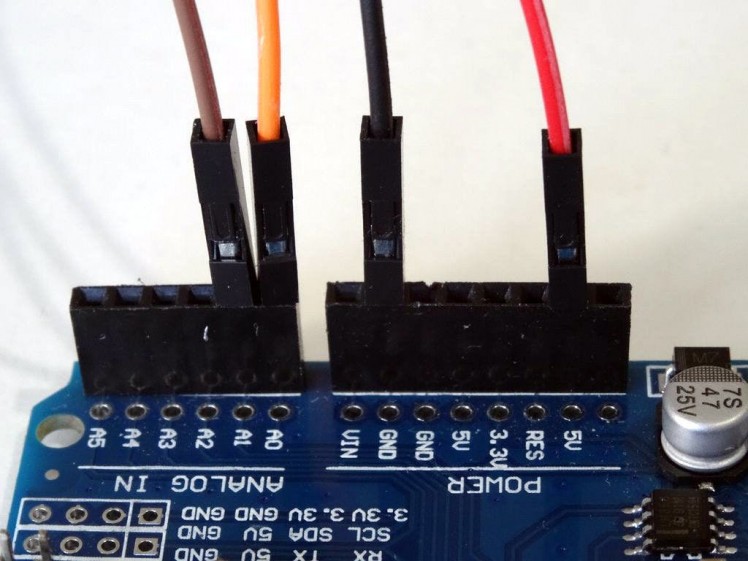
- Connect Female-Female wires to the Ground (black wire), Power (red wire), VRx (brown wire), and VRy (orange wire) of the Joystick as shown in Picture 1
- Connect the VRx wire (brown) the the Analog 1 pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Connect the VRy wire (orange) the the Analog 0 pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Connect the Ground wire (black) to the Ground pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Connect the Power wire (red) to the 5V (Called IOREF on most boards) Power pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
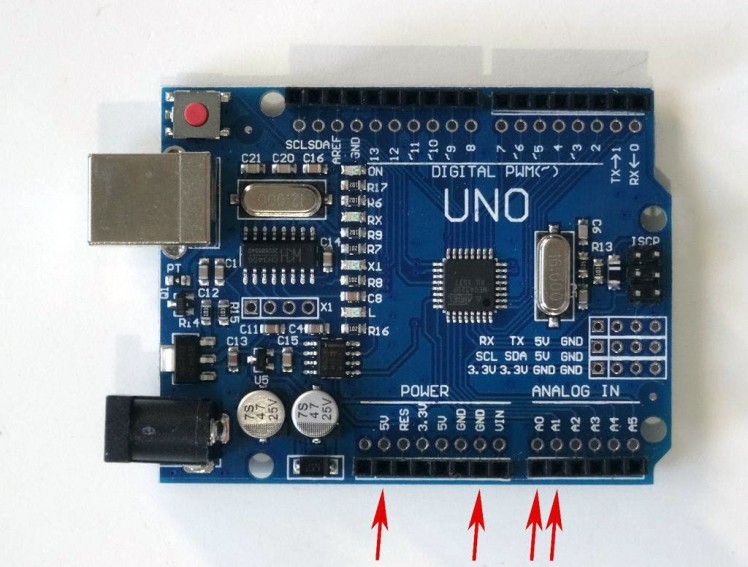
- Picture 3 shows the Arduino Uno pins that were connected in this step
1 / 4 • Picture 1
Picture 1
Picture 2
Picture 3
Picture 4
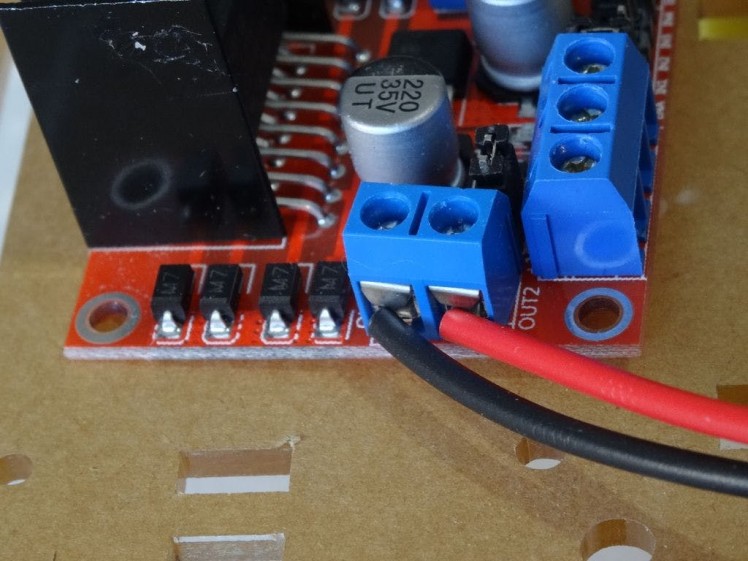
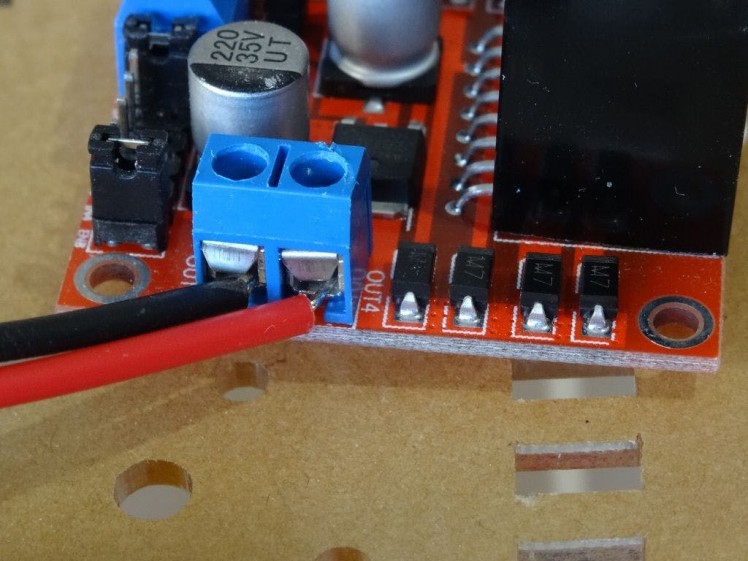
- Connect the wires from one of the motors to the OUT1 and OUT2 Motor Control pins of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1)
- Connect the wires from one of the motors to the OUT3 and OUT4 Motor Control pins of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 2)
- Pictures 3 shows the connected wires to the L298N Motor Driver Module
- Picture 4 shows the other end of the wires connected to the Motors and the 0.1uF anti-sparkingcapacitors soldered to the Motors as shown in this tutorial
1 / 4 • Picture 1
Picture 1
Picture 2

Picture 3
Picture 4
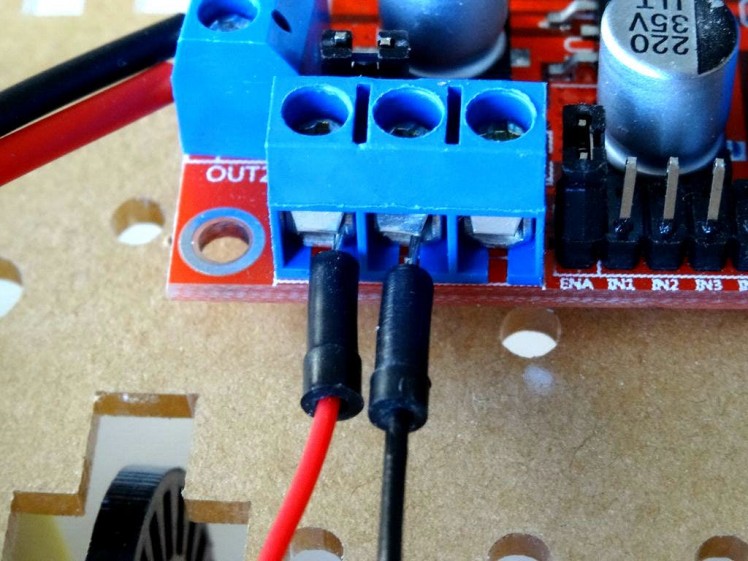
- Connect Male-Male Power wire (red) to the +12V Power Pin of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1 and 2)
- Connect Male-Male Ground wire (black) to the Ground Pin of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1 and 2)
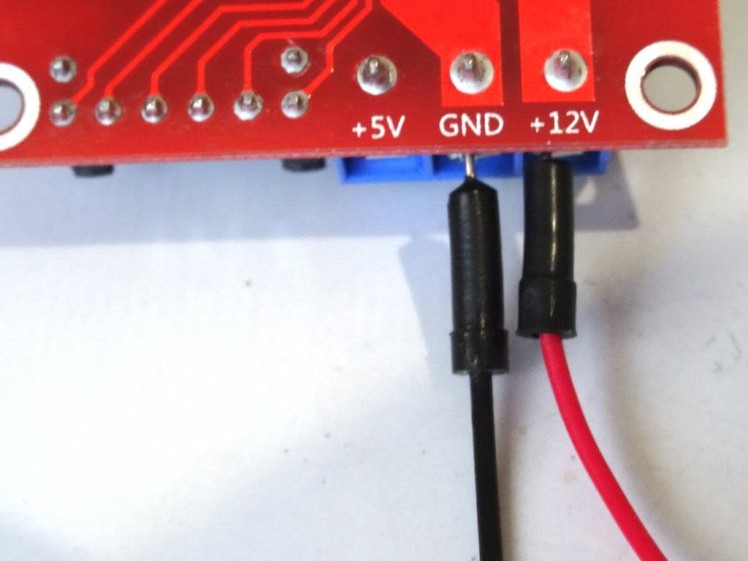
- Connect the other end of the Ground wire (black) to the Ground Pin of the Arduino board (Picture 3)
- Connect the other end of the Power wire (red) to the 5V Power Pin of the Arduino board (Picture 3)
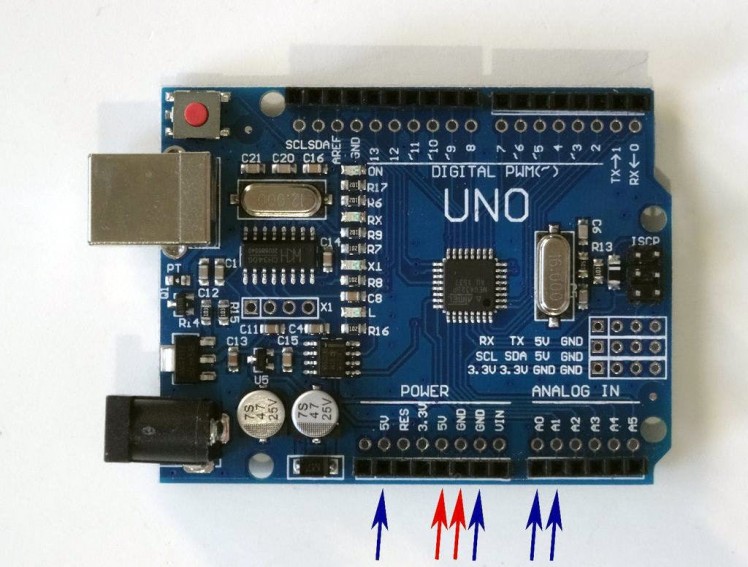
- Picture 4 shows in Red the Arduino Uno pins that ware connected in this step. In Blue are shown the connections done in the previous steps
1 / 3 • Picture 1

Picture 1
Picture 2
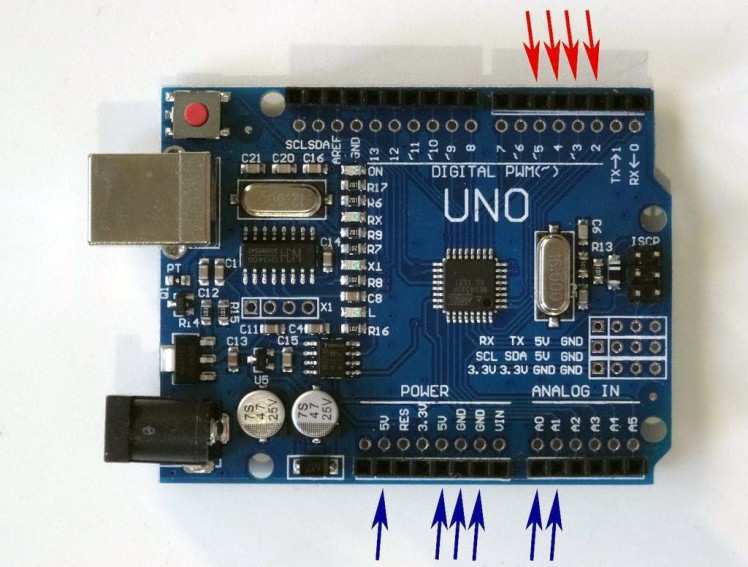
Picture 3
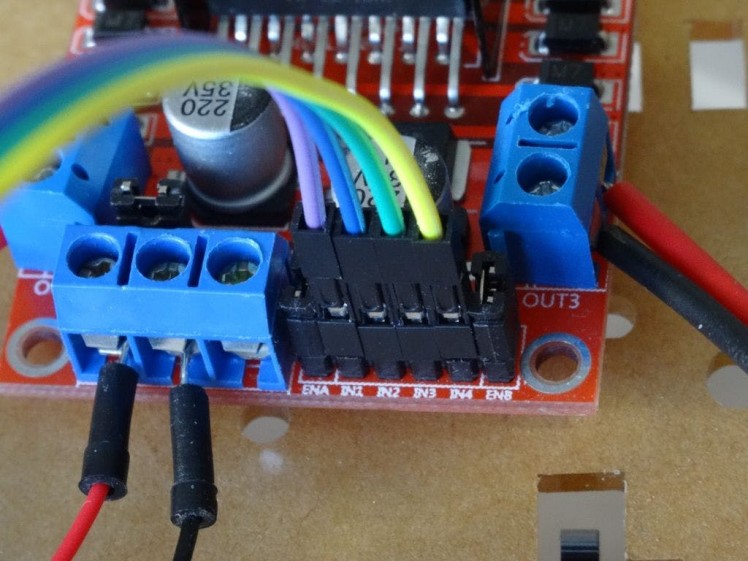
- Leave the ENA and ENB jumpers on the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1)
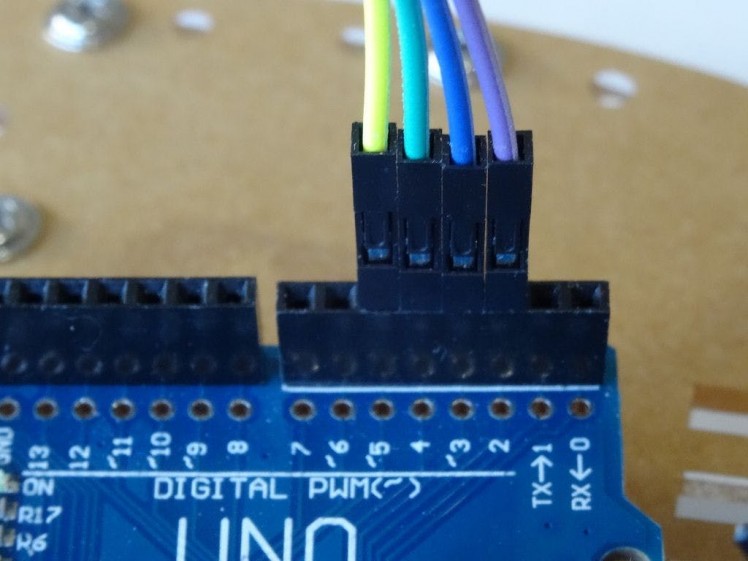
- Connect the Female end of a Female-Male wire (Control 1) (purple wire) to the IN1 pin of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1)
- Connect the Female end of a Female-Male wire (Control 2) (blue wire) to the IN2 pin of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1)
- Connect the Female end of a Female-Male wire (Control 3) (green wire) to the IN3 pin of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1)
- Connect the Female end of a Female-Male wire (Control 4) (yellow wire) to the IN4 pin of the L298N Motor Driver Module (Picture 1)
- Connect the other end of the Control 1 wire (purple) to the Digital 2 Pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Connect the other end of the Control 2 wire (blue) to the Digital 3 Pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Connect the other end of the Control 3 wire (green) to the Digital 4 Pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Connect the other end of the Control 4 wire (yellow) to the Digital 5 Pin of the Arduino board (Picture 2)
- Picture 3 shows in Red the Arduino Uno pins that ware connected in this step. In Blue are shown the connections done in the previous steps
1 / 3 • Picture 1

Picture 1
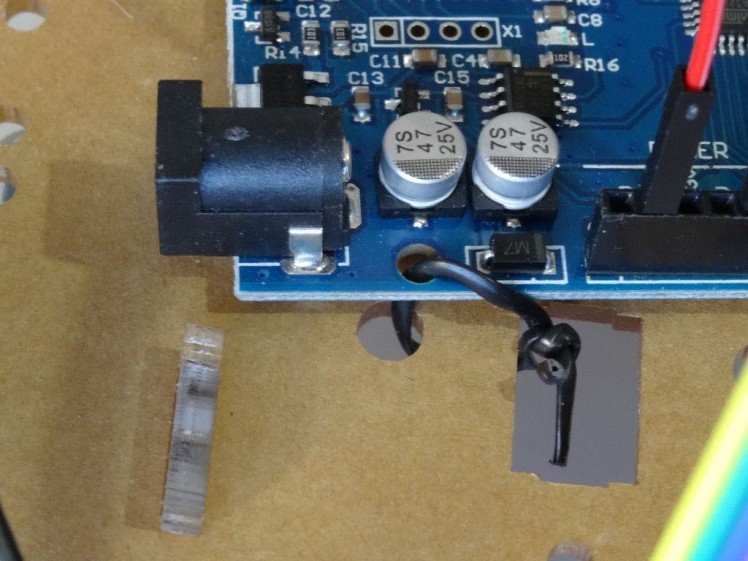
Picture 2
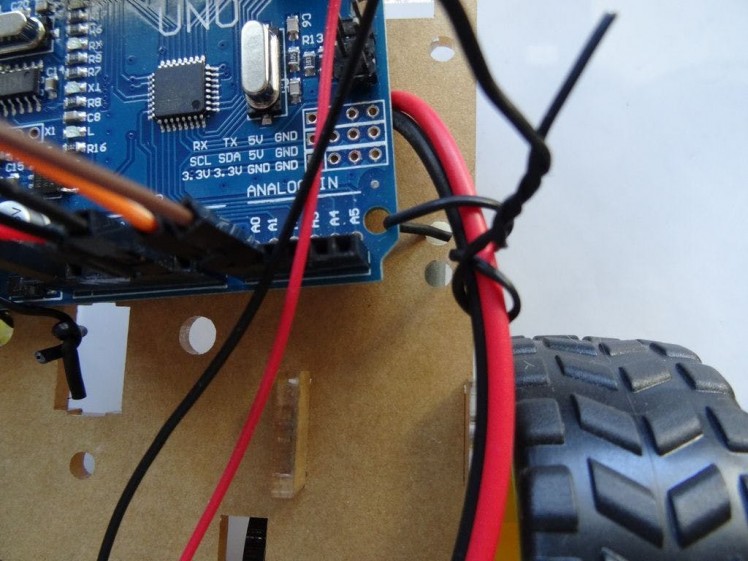
Picture 3
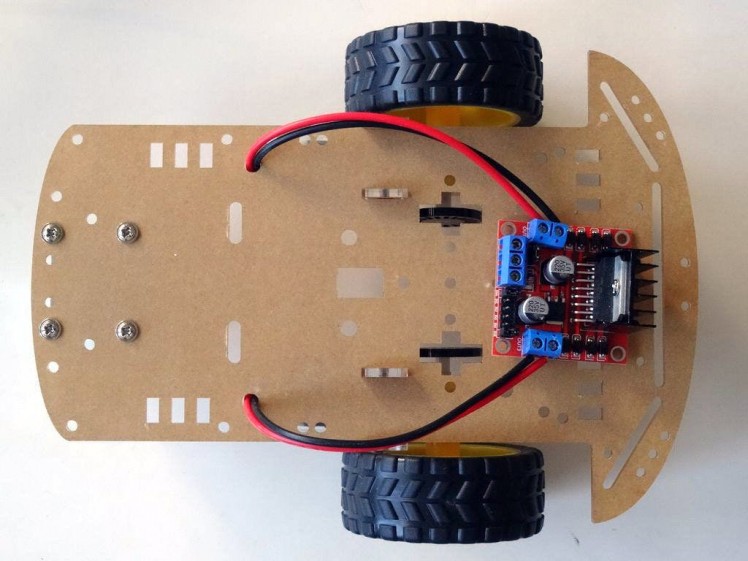
- Add a USB power source (In my case a rechargeable USB power bank) (Picture 1)
- Use straps, rubber bands, screws or any other convenient ways to secure the wires and boards to the chassis (Pictures 1, 2 and 3)
1 / 2 • Picture 1

Picture 1
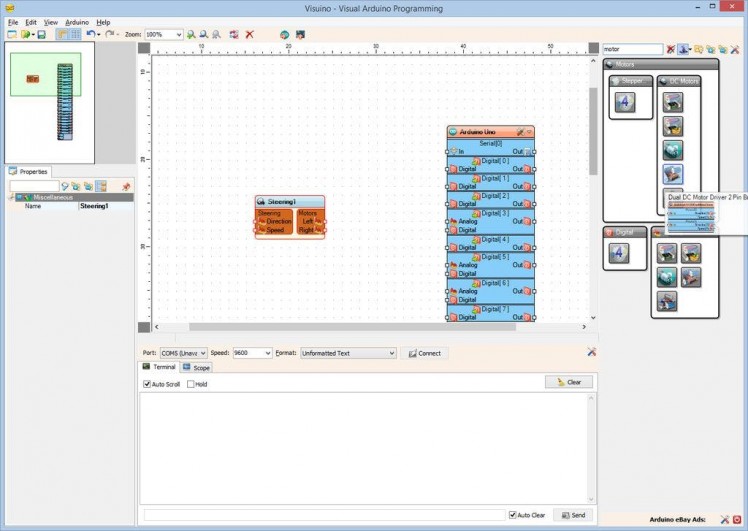
Picture 2
To start programming the Arduino, you will need to have the Arduino IDE installed from here: http://www.arduino.cc/.
Please be aware that there are some critical bugs in Arduino IDE 1.6.6.
Make sure that you install 1.6.7 or higher, otherwise this tutorial will not work!
The Visuino: https://www.visuino.com also needs to be installed.
- Start Visuino as shown in the first picture
- Type "steer" in the Filter box of the Component Toolbox then select the "Steering Differential" component (Picture 1), and drop it in the design area.This component will calculate the speed of the left and right motors based on the Speed and Direction from the Joystick (X and Y control)
- Type "motor" in the Filter box of the Component Toolbox then select the "Dual DC Motor Driver 2 Pin Bridge (L9110S, L298N)" component (Picture 2), and drop it in the design areaSince we left the ENA and ENB jumpers on the L298N Motor Driver module, we will control it with only 2 pins per motor. Visuino also includes a component to control it with the 3 pins, if the jumpers are disconnected, but this is not necessary
1 / 4 • Picture 1
Picture 1
Picture 2
Picture 3
Picture 4
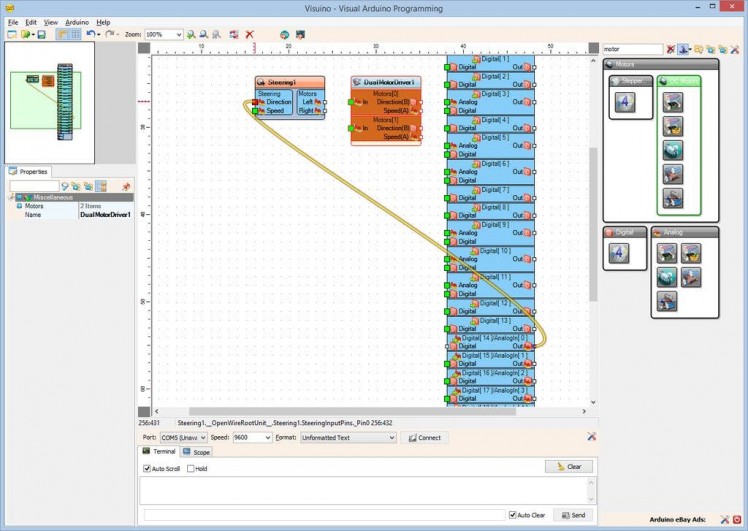
- Connect the Out" pin of "Digital[ 14 ]/AnalogIn[ 0 ]" channel of the Arduino component to the "Direction" input pin of the Steering1 component (Picture 1)
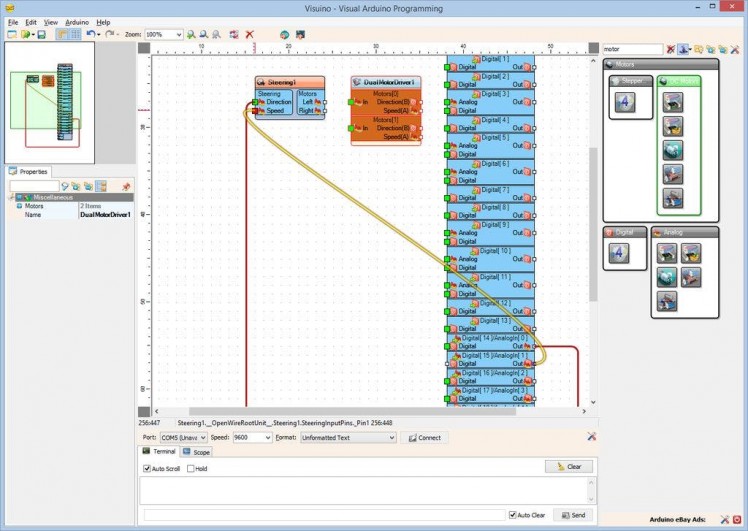
- Connect the "Out" pin of "Digital[ 15 ]/AnalogIn[ 1 ]" channel of the Arduino component to the "Speed" input pin of the Steering1 component (Picture 2)
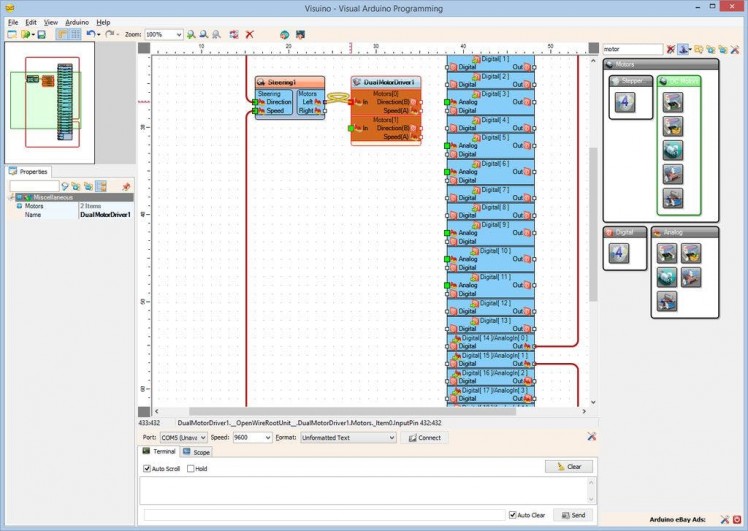
- Connect the "Left" pin of the "Motors" pin list of the Steering1 component to the "In" pin of the "Motors[ 0 ]" channel of the DualMotorDriver1 component (Picture 3)
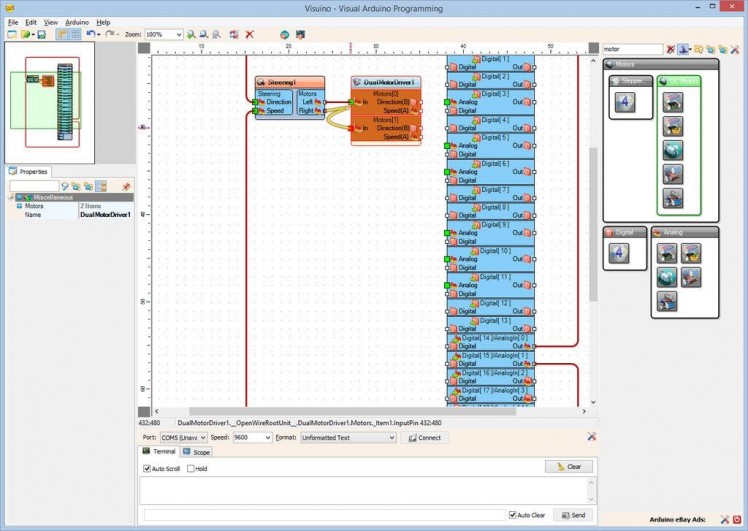
- Connect the "Right" pin of the "Motors" pin list of the Steering1 component to the "In" pin of the "Motors[ 1 ]" channel of the DualMotorDriver1 component (Picture 4)
1 / 4 • Picture 1
Picture 1
Picture 2
Picture 3
Picture 4
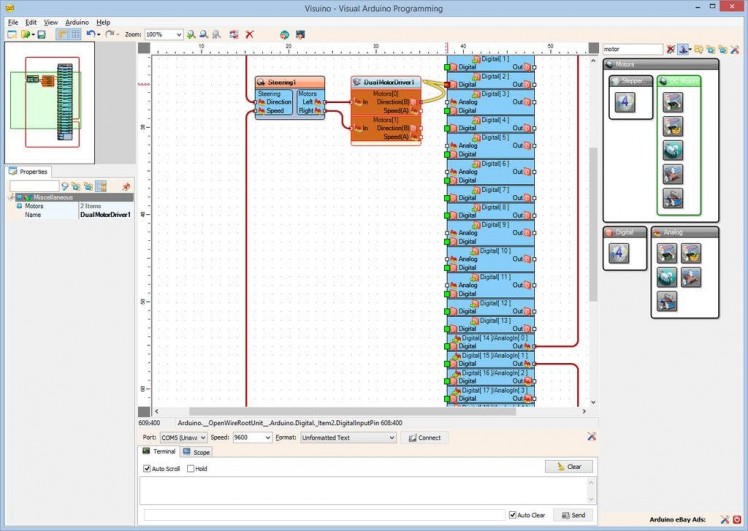
- Connect the "Direction(B)" output pin of the "Motors[ 0 ]" channel of the DualMotorDriver1 component to the "Digital" input pin of "Digital[ 2 ]" channel of the Arduino component (Picture 1)
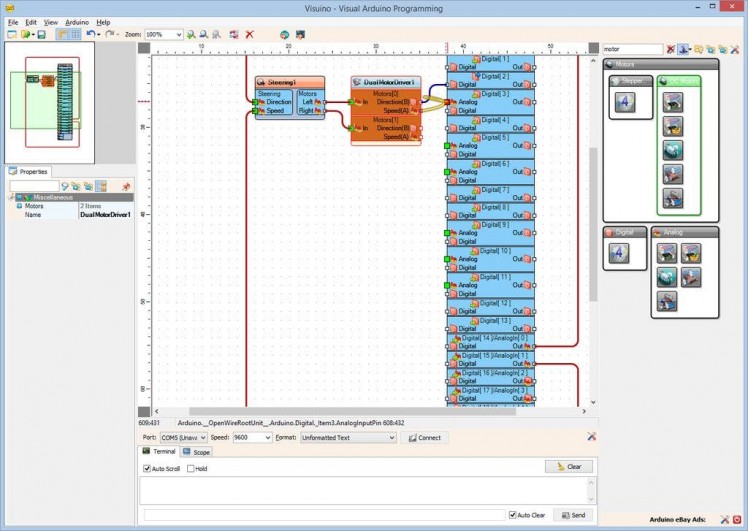
- Connect the "Speed(A)" output pin of the "Motors[ 0 ]" channel of the DualMotorDriver1 component to the "Analog" input pin of "Digital[ 3 ]" channel of the Arduino component (Picture 2)
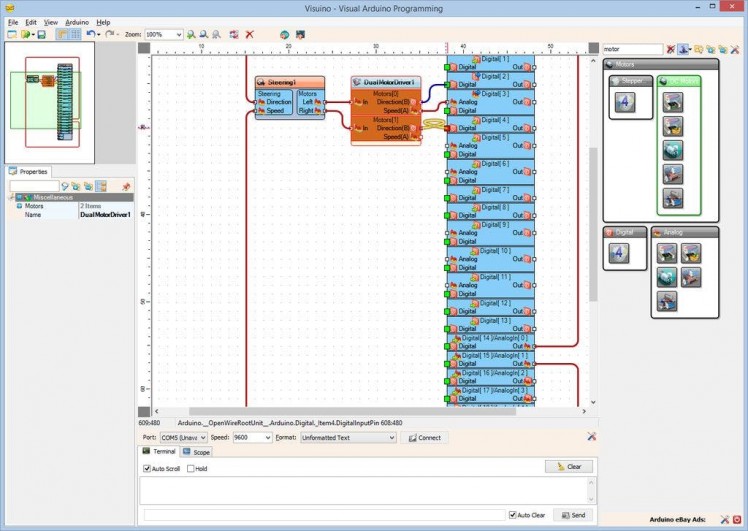
- Connect the "Direction(B)" output pin of the "Motors[ 1 ]" channel of the DualMotorDriver1 component to the "Digital" input pin of "Digital[ 4 ]" channel of the Arduino component (Picture 3)
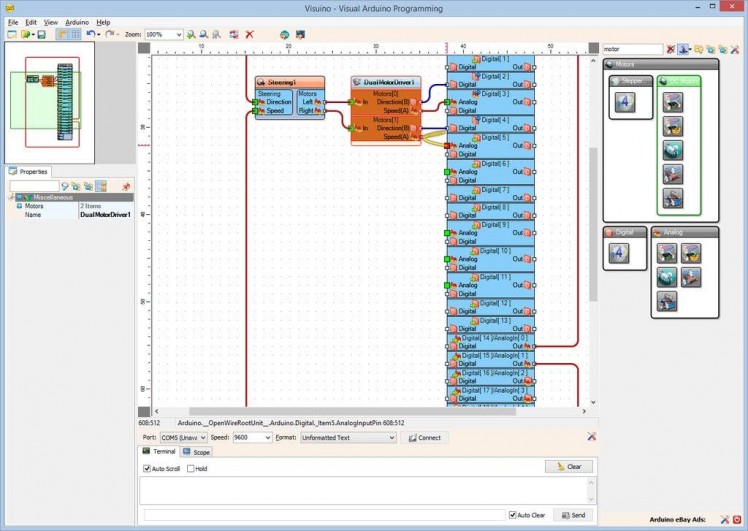
- Connect the "Speed(A)" output pin of the "Motors[ 1 ]" channel of the DualMotorDriver1 component to the "Analog" input pin of "Digital[ 5 ]" channel of the Arduino component (Picture 4)
1 / 2 • Picture 1
Picture 1

Picture 2
- In Visuino, Press F9 or click on the button shown on Picture 1 to generate the Arduino code, and open the Arduino IDE
- In the Arduino IDE, click on the Upload button, to compile and upload the code (Picture 2)
Congratulations! You have completed the project.
The Video shows the connected and powered up Smart Car.
If you connect the Power to the Arduino board, you can use the Joystick to control the car by moving the Joystick forward and backward the car will move in the Forward or Backward direction, and moving the Joystick left and right will make the car turn left and right.
If the car is not moving as expected, you may need to swap the wires controlling the motors connected in Step 3 to make them rotate in the proper direction.
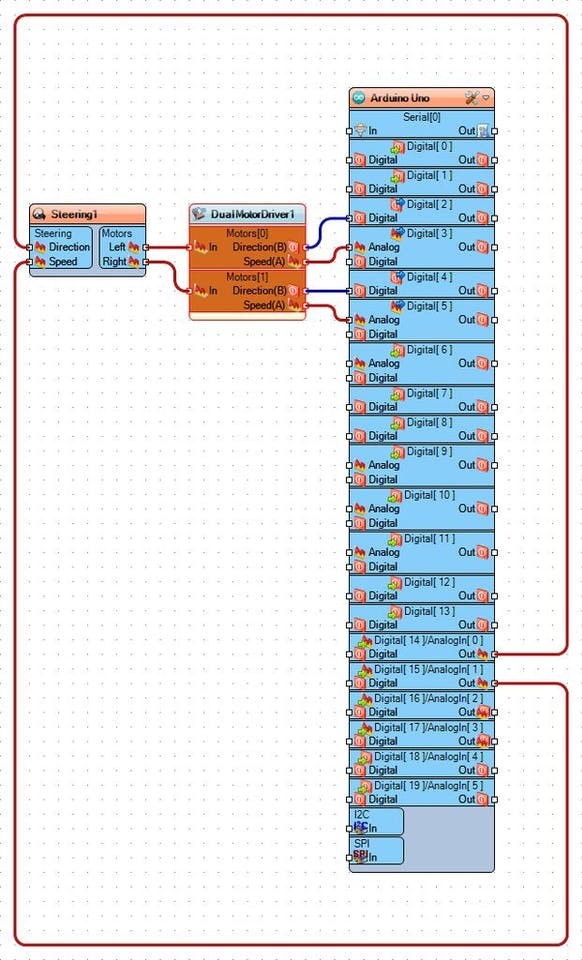
On the Picture you can see the complete Visuino diagram.
Also attached is the Visuino project, that I created for this Tutorial. You can download and open it in Visuino: https://www.visuino.com