The Advantages of Binary Code Modulation in LED Lighting
Binary Code Modulation (BCM) presents an innovative approach to controlling LED brightness, differing from the commonly used Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). While PWM adjusts brightness by rapidly toggling the LED on and off based on a duty cycle, BCM leverages binary values to produce varying intensities of light. Each bit in a binary code sequence carries a weighted influence, determining how long the LED stays illuminated versus off. This results in a more efficient and granular brightness control system.

Watch Ian talk about Binary Code Modulation in this episode of The Electromaker Show
One key advantage of BCM is its scalability. It allows for the control of multiple LEDs with minimal processor overhead, making it ideal for projects requiring large arrays of LEDs or when conserving processing power is essential. As such, BCM is a compelling choice for complex LED control projects that demand efficiency and precision.
Comparing PWM and BCM for LED Dimming
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is widely used for controlling the brightness of LEDs, where the light intensity is determined by the ratio of time the LED is on versus off, commonly referred to as the duty cycle. The longer the on-time, the brighter the LED appears. This method has been the standard due to its simplicity and effectiveness.
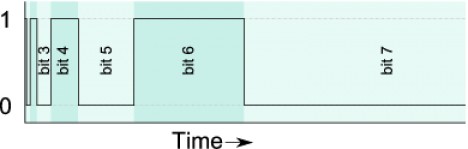
Binary Code Modulation (BCM), however, offers an alternative that assigns specific on-off durations based on binary values. Unlike PWM, which requires constant microcontroller attention, BCM uses binary bits to dictate the brightness, making it more efficient. This method allows for precise brightness control with fewer demands on the processor. In particular, BCM is ideal for controlling large LED arrays or in scenarios where microcontroller processing power is limited.
By using binary representation, each bit has a weighted influence on the brightness, allowing for a range of intensities to be achieved with minimal resources. This makes BCM particularly suitable for applications where scalability and processor efficiency are critical.
Practical Applications of BCM in LED Control
Binary Code Modulation (BCM) proves highly effective in scenarios where numerous LEDs need to be controlled simultaneously. One of the key strengths of BCM lies in its ability to manage large LED arrays with minimal computational load. In a typical 4-bit system, for instance, each bit carries double the weight of the previous one, enabling a broad spectrum of brightness levels with fewer interruptions. This allows for fine control over LED brightness, offering significant flexibility in display and lighting applications.
BCM’s scalability also makes it an efficient choice for tasks where the microcontroller needs to handle multiple operations concurrently. Since the control of LED brightness relies on binary sequences, the microcontroller can focus on other processes while still maintaining consistent lighting outputs. Projects that have employed BCM showcase its ability to control large LED setups with minimal flickering or delays, demonstrating its potential in both hobbyist and professional lighting projects.
This technique is particularly useful in fields such as signage, display boards, and decorative lighting, where controlling multiple LEDs without taxing the processor is essential for smooth operation.
Did you enjoy this article?
Make sure you subscribe to The Electromaker Show for similar content and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!













































Leave your feedback...