Temperature Sensor Modules (2022 Buyer's Guide)
Temperature sensors are directly or in-directly integrated into thermostats, water heaters, or even environmental sensing monitors. The temperature sensor module is a piece of hardware primarily used to measure the surrounding temperature and convert it into a readable unit. Suppose you are planning to implement a small IoT project for environmental sensing. In that case, it is likely that you’d require a temperature sensor along with humidity, smoke, air pressure, and gas sensors.
Other than compatibility, specific parameters should be considered when choosing a temperature sensor module. Some of them include the temperature range it can support. For measuring air temperature and water temperature, there are different requirements for the temperature range and hence the type of sensor you’d want to interface will change. Other factors include the temperature sensor module’s accuracy and stability, which should measure the accurate temperature with a low error percentage. Depending on its deployment, the size and packaging of the module will be decided. There are several breakout boards that provide added functionalities but come at the cost of packaging size, whereas some temperature sensors are also in the size of a transistor (IC).

How does a temperature sensor work?
The basic idea of measurement in temperature sensors depends on the voltage across the diode terminal; as voltage increases, the temperature also increases. If there is a voltage drop between the transistor terminals, the temperature decreases. However, different temperature sensors have other operating principles, as a few of them work on the principle of stress change due to temperature change.
What are the different types of temperature sensors?
There are different types of temperature sensor modules categorized on the basis of contact and non-contact sensors. A contact-type temperature sensor means measuring an object is done by being in direct contact with it. In contrast, for a non-contact type temperature sensor, the measurement is performed through radiation emitted by the heat source.
Thermostat temperature sensor
A thermostat is one of the contact-type temperature sensors that consist of a bi-metallic strip of two dissimilar metals. The difference in the coefficient of the linear expansion of both metals causes them to produce a mechanical bending movement that is subjected to heat. In terms of smaller packaging, a thermistor consists of a sensing element with two wires that can be connected to the electric circuitry. They measure temperature by measuring the change in resistance of the electric current.
Resistive temperature detectors
In resistive temperature detectors (RTDs), the sensor is constructed from conducting elements like platinum with an operating principle depending on temperature variation. They work similarly to the thermistors as they are connected to a circuit but have a much wide range of temperature sensing and can be used for extreme temperature settings. In thermocouples, the two conductors are made up of different metals connected to form a junction. This junction is subjected to heat which changes the voltage directly proportional to the temperature input.
Now, let us look at some of the must-use temperature sensor modules that you should buy for your IoT environmental sensing applications.
Grove Temperature Sensor
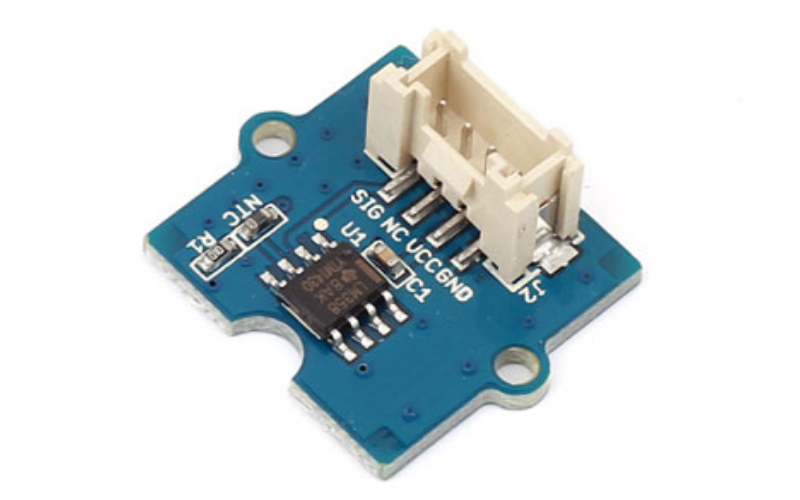 As grove sensor modules have become popular in the Seeed Studio hardware ecosystem, their improved compatibility with other development boards makes them a good choice for your application. The Grove temperature sensor uses a thermistor that returns the ambient temperature in the form of a resistance value. The onboard circuitry converts the varying voltage measured by an analog input pin to a temperature. The operating range is -40 to 125°C, with an accuracy of 1.5°C.
As grove sensor modules have become popular in the Seeed Studio hardware ecosystem, their improved compatibility with other development boards makes them a good choice for your application. The Grove temperature sensor uses a thermistor that returns the ambient temperature in the form of a resistance value. The onboard circuitry converts the varying voltage measured by an analog input pin to a temperature. The operating range is -40 to 125°C, with an accuracy of 1.5°C.
Specifications of Grove Temperature Sensor
- Type: Seeed Studio Grove temperature sensor
- Operating temperature: -40 to +125°C
- Supply voltage: 3.3 to 5V
- Resistance Tolerance: ±1%
Adafruit DS18B20 Digital Temperature Sensor
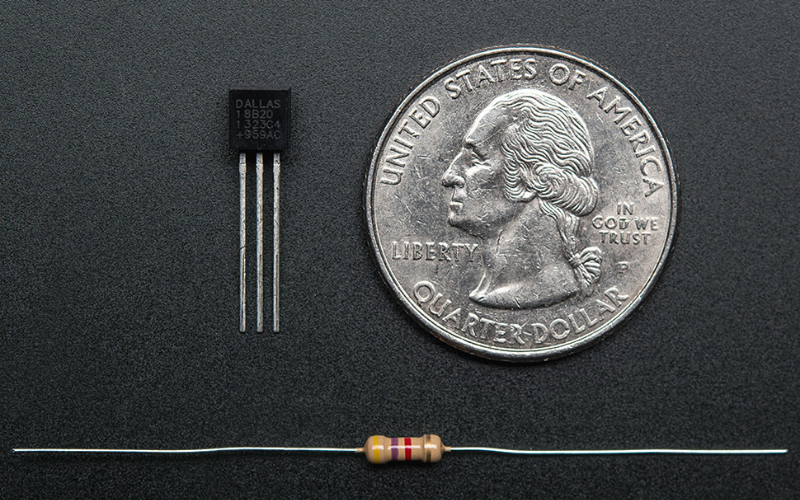
This transistor-looking Adafruit digital temperature sensor is made to this list because of its accuracy and precision for measuring the ambient temperature with the precision of ±0.5°C with 12-bits of precision from the onboard DAC. Easy compatibility with any microcontroller using a single digital pin is also known as the 1-wire digital temperature sensor with a unique 64-bit ID burned in at the factory.
Specification of Adafruit DS18B20 Digital Temperature Sensor
- Temperature range: -55 to 125°C
- Interface: 1-Wire interface- requires only one digital pin for communication
- Connectivity: Multiple sensors can share one pin
- Accuracy: ±0.5°C Accuracy from -10°C to +85°C
- Query time: less than 750ms
- Power supply: 3.0V to 5.5V
Adafruit TMP235 Temperature Sensor
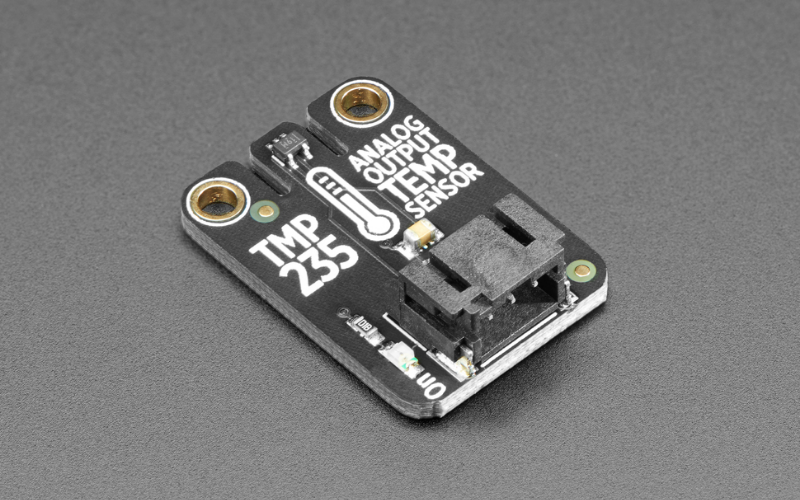
One of the essential things to note about the Adafruit TMP235 temperature sensor is that it gives an analog output and not I2C. This means it is a good choice for interfacing with any microcontroller with an analog output providing flexibility to the user. With STEMMA QT connectors, the plug-and-play option makes it simple to use without the need for custom libraries. The hardware sensor offers a decent accuracy range of ±1.2°C with a voltage of 0V at 50°C and 1.75V at 125°C.
Specifications of Adafruit TMP235 Temperature Sensor
- Accuracy: ±1.2°C
- Operating temperature: -50°C to 125°C
- Output type: Analog
- Connector: STEMMA connectors
- Dimensions: 25.5x17.7x7.2 mm
Gravity: I2C High Temperature Sensor
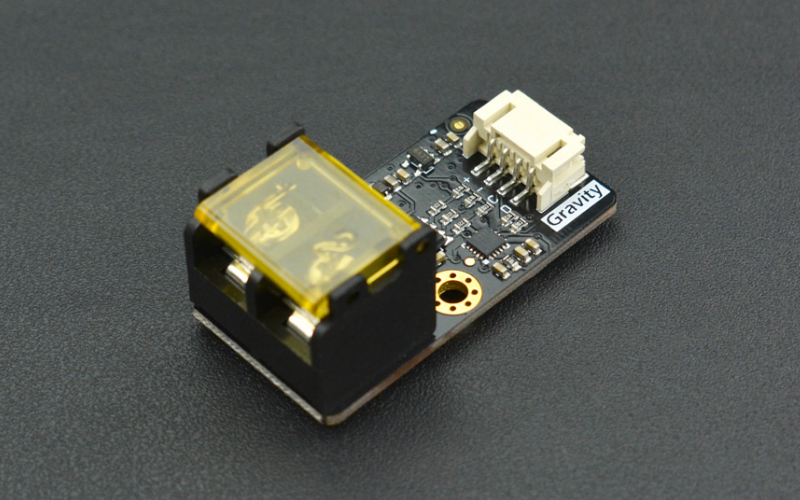

DFRobot’s I2C high-temperature sensor is on the list because of its large temperature sensing range. The hardware is capable of sensing from a temperature of -270°C to 1372°C with a resolution of 0.25 °C and error ranging from ≤ ±2°C to ±4°C. The error margin for this temperature might seem more, but the temperature range it can sense is might larger than any other product on the list. The hardware sensor uses MAX31855K dedicated chip to amplify the small voltage and convert it into digital signals.
Specifications of Gravity I2C High-Temperature Sensor
- Type: K Type Thermocouple
- Temperature range: -270°C to 1372°C
- Accuracy: ≤ ±2°C(-200°C~700°C) and ±4°C(700°C~1350°C)
- Resolution: 0.25 °C
- Power supply: 3.3V to 5.5V
- Interfaces: Gravity I2C
- Dimensions: 44x22 mm
Gravity: I2C Non-Contact IR Temperature Sensor
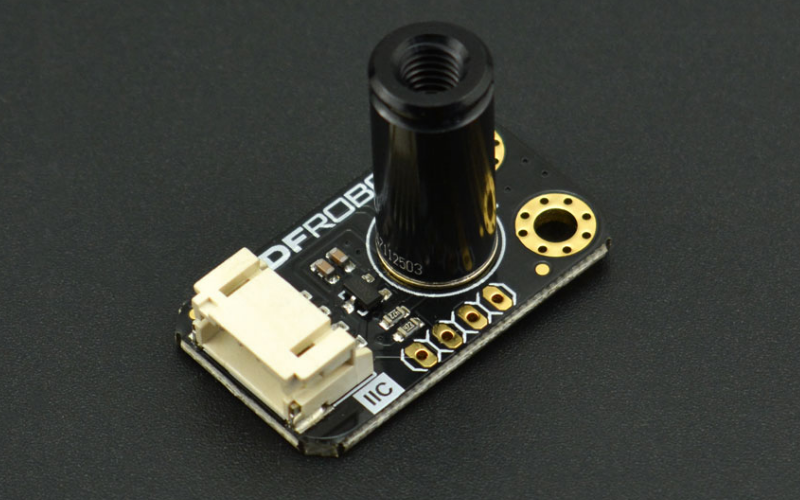

Another temperature sensor from DFRobot comes under a non-contact sensor integrated with an infrared temperature measurement module– MLX90614. The module is capable of sensing the surface temperature by detecting infrared radiation energy and wavelength distribution. The hardware sensor has a temperature sensing range of 70.0°C below freezing point and 270°C above with a resolution of 0.01°C.
Specification of I2C Non-Contact IR Temperature Sensor
- Module: MLX90614-DCI
- Operating temperature: -70.01°C to +270°C
- Resolution: 0.01°C
- Power supply: 3.3V - 5V
- Interface: I2C
- Dimensions: 31.5x18 mm
- Weight: 15g
Final thoughts on temperature sensor modules
As mentioned in the introduction, the choice of temperature sensor depends on various factors from scalability, accuracy, temperature sensing range, packaging, and size of the module. For large temperature sensing, you can consider buying the DFRobot high-temperature sensor while for high precision and small form factor sensor, Adafruit DS18B20 digital temperature sensor can make a good option.
Your turn: Let us know which one would you choose and why in the comments section below...














































Leave your feedback...