Poly LMN: The Liquid Metal Revolutionizing Flexible Circuits
Stretchable PCBs are paving the way for new innovations in flexible electronics, opening up possibilities in fields like soft body robotics, wearable devices, and advanced sensors. One of the key technologies behind this breakthrough is the use of Poly LMN, a liquid metal substrate that offers flexibility and adaptability in circuit design. Unlike traditional solder paste, Poly LMN allows for the creation of circuits that can stretch and bend, enabling new functionalities in electronic devices that need to conform to various shapes and movements.
Watch Ian talk about CNLohr PolyLMN testing in this episode of The Electromaker Show
This flexibility provides numerous advantages for engineers working on projects that require lightweight, durable, and customizable circuit designs. The technology, demonstrated in research settings, shows great potential for practical applications, particularly in environments where rigid boards may not be suitable, such as in soft robotics or pressure-sensitive touchpads.
Advantages and Applications of Liquid Metal Substrates
Poly LMN, a liquid metal substrate, offers a revolutionary alternative to traditional solder paste in the creation of flexible circuit boards. By applying this compound using a solder mask and curing it in an oven, engineers can create circuits that are both stretchable and durable. This method simplifies the circuit-making process, allowing for enhanced flexibility without compromising on performance.
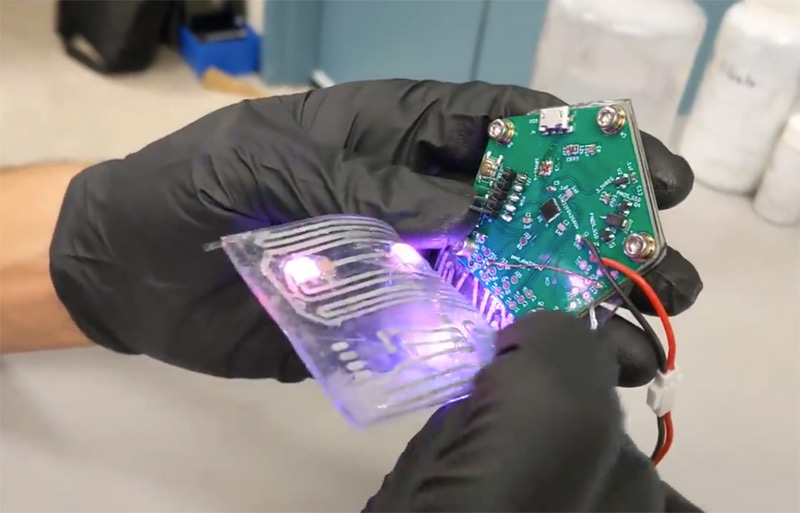
One notable application of Poly LMN is in touch-sensitive PCBs. These circuits, when combined with pressure-sensitive touchpads, enable dynamic control of electronic devices. For example, varying the pressure on a touchpad can alter the brightness of LEDs. Additionally, flexible PCBs can be adapted for use as antennas, demonstrating their versatility in both consumer electronics and industrial research.
Experimentation and Future Potential
In recent experiments, researchers have demonstrated how flexible PCBs, created using Poly LMN, can be applied to various advanced projects. A research team working with these materials spent time in the lab testing the potential of flexible circuits in unique ways. For example, one project involved using flexible PCBs as antennas to transmit FM radio signals to a computer, showcasing their adaptability beyond traditional uses.
These experiments highlight the future potential of stretchable electronics, where flexible circuit designs could pave the way for innovations in robotics, medical devices, and more.
The development of stretchable PCBs using Poly LMN marks a significant step forward in flexible electronics. By enabling new possibilities for applications such as soft robotics and flexible sensors, this technology provides engineers with more versatile tools for creating innovative devices. As demonstrated through various experiments, the potential for further advancements is vast, with flexible circuits showing promise in numerous fields from industrial research to consumer electronics.
Did you enjoy this article?
Make sure you subscribe to The Electromaker Show for similar content and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!














































Leave your feedback...