How Stretchable PCBs Are Shaping the Future of Wearables and Robotics
Stretchable PCBs are the next frontier in flexible electronics, offering new possibilities in wearables, robotics, and more. Unlike traditional flexible PCBs, which can bend, stretchable PCBs maintain their functionality even when elongated. Research at Yale University’s Faboratory has been pivotal in exploring this technology, allowing circuits to be stretched up to four times their original size. This advancement opens doors to innovations in areas like soft robotics, where flexibility is crucial for performance.
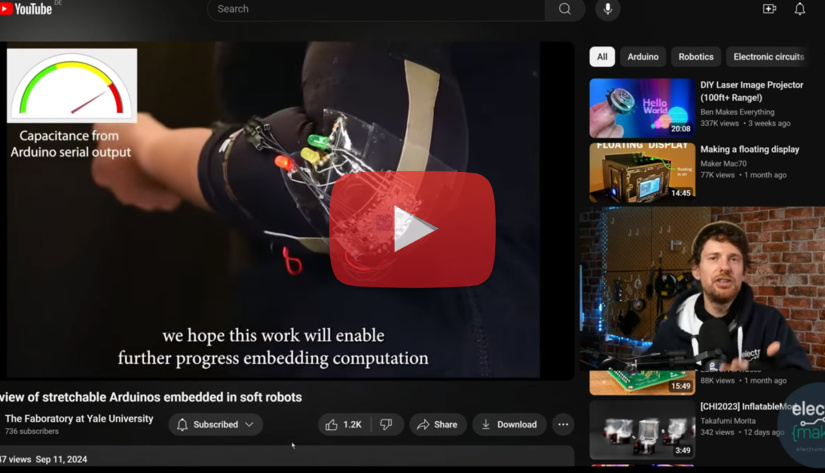
Watch Ian talk about stretchable Arduinos embedded in soft robots in this episode of The Electromaker Show
The concept of stretchable electronics builds upon existing technologies like FlexDuino, which has been highlighted in past projects for its role in wearables. Stretchable PCBs take this a step further, making it possible to integrate sensors and controllers directly into stretchable materials. This approach enables a more seamless integration into applications requiring both flexibility and durability.
Real-World Applications of Stretchable PCBs
One of the most exciting applications of stretchable PCBs comes from their use in soft-body robots. Researchers at Yale University’s Faboratory demonstrated how these flexible circuits can be integrated into soft robots, allowing the entire control system to be placed directly on the robot itself. By using a special blend of metal paste and stretchable materials, these PCBs can stretch without losing their electrical properties, which is key for robots that require flexibility for movement and interaction.
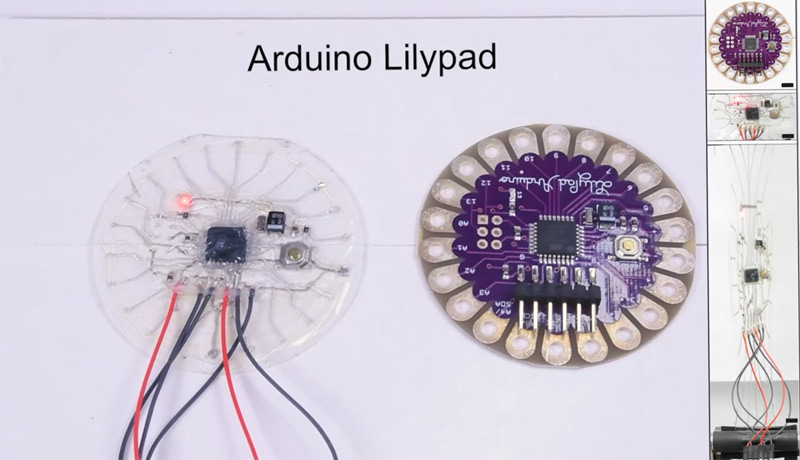
For instance, in one demonstration, a stretchable PCB was applied to an Arduino LilyPad and paired with a sound sensor, enabling the robot to react to its environment. This allows the robot to carry all necessary sensors on board, reducing the need for external components. Additionally, stretchable PCBs can be used in medical devices, such as wearable sensors that monitor vital signs in real time, offering unprecedented flexibility in design.
Future of Flexible Sensors and Wearables
The potential of stretchable PCBs extends beyond robotics and into the world of wearable technology. One example from the Yale research team showcases a fully flexible sensor designed to be worn on a person’s elbow. This sensor, with a microcontroller positioned at the point of strain, demonstrates how stretchable electronics can adapt to complex movements while still maintaining functionality. Such innovations are ideal for wearables that need to conform to the human body’s natural motion.
With flexible sensors, applications in healthcare become more feasible. These stretchable circuits can monitor muscle movements, detect strain, or measure vital signs in real time. The integration of PCBs into soft, flexible materials allows devices to be more comfortable and less intrusive, marking a significant step forward in both the medical and consumer wearable markets. Ongoing research continues to explore ways to make these technologies more robust, efficient, and scalable.
Stretchable PCBs are set to transform industries from robotics to wearables. By enabling circuits to stretch and maintain functionality, researchers have opened up new possibilities for flexible electronics in both consumer and industrial applications. From soft-body robots to medical sensors, the integration of these stretchable circuits will play a crucial role in shaping the future of technology.
Did you enjoy this article?
Make sure you subscribe to The Electromaker Show for similar content and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!













































Leave your feedback...