Bluetooth 6.0 Gets Smarter: Channel Sounding for Secure Distance Measurement - Embedded World 2025
At Embedded World 2025, Nordic Semiconductor demonstrated Channel Sounding—part of the Bluetooth 6.0 specification—which enables precise distance measurement using Bluetooth signals. Rather than relying on time-of-flight, this method uses phase shift across multiple frequencies to calculate distance. The same principle is used in astrophysics to measure vast distances in space.
The live demo showcased a hardware setup transmitting Bluetooth packets between devices and calculating real-time proximity using this new approach. Nordic confirmed that Channel Sounding will be supported in their upcoming nRF54L and nRF54H Series SoCs, laying the groundwork for broader adoption in commercial products.
Accuracy, Security, and Real-World Applications
According to the Bluetooth SIG, Channel Sounding enables accuracy down to 0.5 metres, with custom algorithms potentially improving that to just 10 cm. This opens new possibilities in secure access control, especially for automotive and smart home use cases.
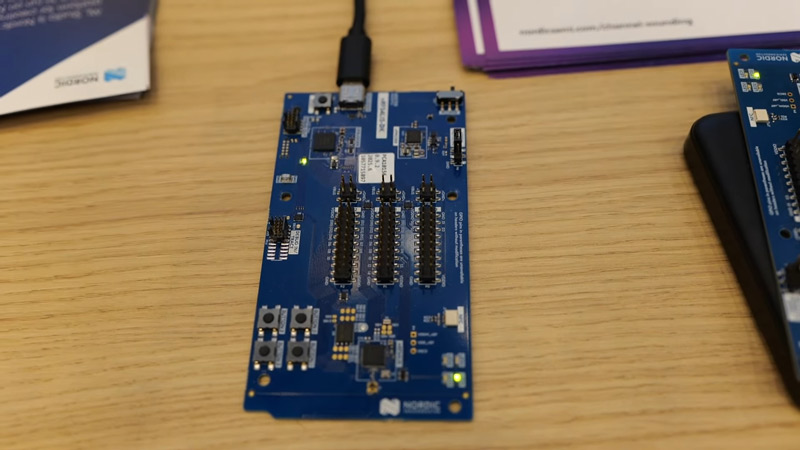
One example demonstrated at the booth was a phone unlocking a car door only when the user is within a safe distance. This level of precision prevents early unlocking and enhances security, especially in shared or public environments like car parks. Nordic noted that the automotive industry has played a significant role in pushing for this feature in future Bluetooth chips.
Smart locks and home automation are other promising applications. The improved proximity detection offers a smoother user experience compared to conventional Bluetooth signal strength detection.
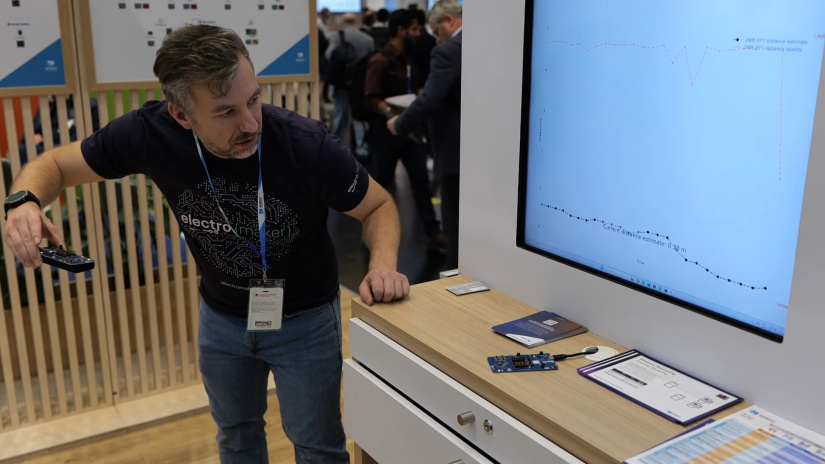

Overcoming Challenges with Custom Algorithms
Traditional Bluetooth ranging can be disrupted by signal interference or reflections. Channel Sounding helps mitigate this by focusing on signal phase rather than strength. However, complex environments—like those with metal surfaces—may still present challenges.
To handle this, developers can build custom algorithms outside the Bluetooth spec, optimising for specific use cases. Nordic’s flexible development tools support this approach, allowing engineers to fine-tune solutions as needed. While triangulation with multiple nodes is technically possible, it’s not the primary use case for the current spec.
Did you enjoy this article?
Make sure you subscribe to The Electromaker Show for similar content and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!













































Leave your feedback...