ASUS Tinker Board vs Raspberry Pi
The Raspberry Pi reigns supreme as the most popular single-board computer (SBC) available. However, plenty of Raspberry Pi alternatives exist. Among the most popular is the ASUS Tinker Board. Like the Raspberry Pi, the ASUS Tinker Board runs many of the same operating systems (OSes), comes in a similar form factor, and may be used for loads of projects. Learn all about the ASUS Tinker Board vs. Raspberry Pi in this single-board computer head-to-head!
What is the Raspberry Pi?
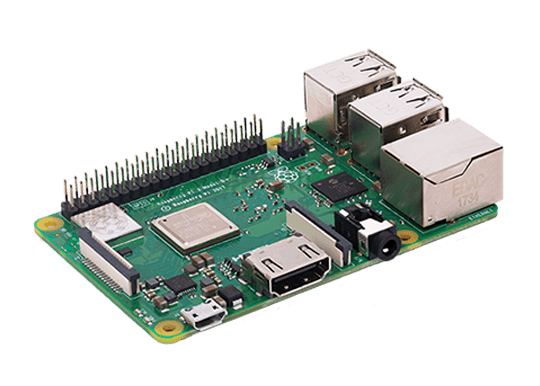
From the Raspberry Pi Foundation comes the Raspberry Pi. It's a set of maker boards capable of many different projects, from a smart home hub to retro gaming console, and robotics. Since its inception, the Raspberry Pi underwent several hardware refreshes and now comes in the Raspberry Pi 4 variant, as well as Raspberry Pi Zero and Zero W boards. The Raspberry Pi 0/W, while carrying reduced processing power, benefits from a much lower price tag. Essentially, the Raspberry Pi is just a mini-computer which comes with all components baked-in. RAM, CPU, and GPU are all built into the board. Simply add a microSD card with a compatible operating system and you're ready to go.
What is the ASUS Tinker Board?
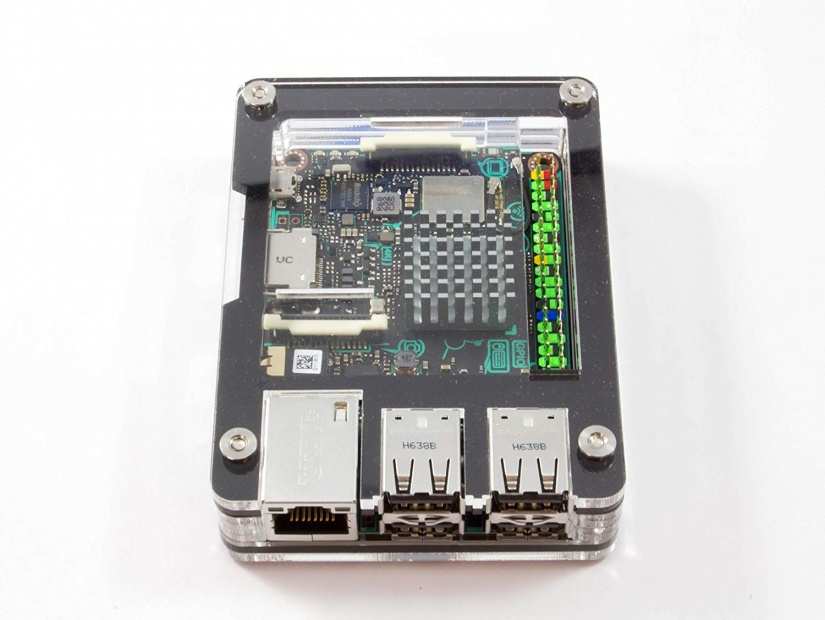

Like the Raspberry Pi, the ASUS Tinker Board is a development board suitable for a variety of purposes. You can install a Linux operating such as Ubuntu or Debian for a basic desktop, or a specialized Linux distro. It's powered by a Mali T764 GPU and touts impressive computing power that can handle UHD video playback. The Tinker Board remains perfect for a bevy of Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Raspberry Pi vs ASUS Tinker Board Specs
When comparing the ASUS Tinker Board and Raspberry Pi, an excellent starting spot is hardware. Both boards come in multiple versions. For the ASUS Tinker Board, you can opt for the base Tinker Board or the ASUS Tinker Board S. Raspberry Pi boards come in the Raspberry Pi Zero/Zero W, Raspberry Pi A+, Raspberry Pi 3 B+, and Raspberry Pi 4.
The Raspberry Pi 3 B+ boasts an HDMI out, 40-pin GPIO header, Broadcom BCM28730B0 quad-core A53 ARMv8 64-bit system on a chip (SoC0, and 3.5mm audio-video jack. You'll find four USB 2.0 ports, Ethernet, a camera serial interface (CSI), Bluetooth 4.3 BLE, and 802.11b/g/n/ac Wi-Fi. Similarly, the Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ virtually the same specs. However, its RAM module is cut in half with 512MB of RAM. It also features a smaller footprint. The Raspberry Pi Zero arrives as the tiniest Raspberry Pi board. Since it's intended for IoT projects, hardware is pretty barebones. There's a 1GHz single-core CPU, 512MB of RAM, a HAT-compatible 40-pin header, mini HDMI, and CSI camera connector. Meanwhile the Raspberry Pi Zero W sports similar specs but adds 802.11 b/g/n wireless as well as Bluetooth 4.1 BLE connectivity.
At the core of the ASUS Tinker Board is a Cortex A17 quad-core 1.8GHz processor, 2GB DDR3 RAM, a microSD card slot, Gigabit LAN, 802.11 b/g/n WI-Fi, Bluetooth 4.0, and a 40-pin GPIO header. The form factor is virtually identical to that of the Raspberry Pi, so the Tinker Board is compatible with Pi cases. The Tinker Board S is identical to its older sibling, adding a 16GB eMMC module, HDMI CEC, 2-pin power-on header, low voltage input detection support, and auto-switch plus plug-in detection.
Raspberry Pi 4 Specs
- Broadcom BCM2711, Quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.5GHz
- 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB of LPDDR4-2400 SDRAM (depending on model)
- 2.4 GHz and 5.0 GHz IEEE 802.11ac wireless, Bluetooth 5.0, BLE
- Gigabit Ethernet
- 2 USB 3.0 ports; 2 USB 2.0 ports.
- Raspberry Pi standard 40 pin GPIO header (fully backwards compatible with previous boards)
- 2 × micro-HDMI ports (up to 4kp60 supported)
- 2-lane MIPI DSI display port
- 2-lane MIPI CSI camera port
- 4-pole stereo audio and composite video port
- H.265 (4kp60 decode), H264 (1080p60 decode, 1080p30 encode)
- OpenGL ES 3.0 graphics
- MicroSD card slot for loading operating system and data storage
- 5V DC via USB-C connector (minimum 3A*)
- 5V DC via GPIO header (minimum 3A*)
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) enabled (requires separate PoE HAT)
- Operating temperature: 0 – 50 degrees C ambient
Raspberry Pi 3 B+ specs:
- Broadcom BCM2837B0 quad-core A53 (ARMv8) 64-bit @ 1.4GHz SoC
- 1GB LPDDR2 SDRAM
- Gigabit Ethernet, 802.11b/g/n/ac Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth 4.2
- microSD storage
- 40-pin GPIO header
- HDMI port, 3.5mm A/V jack
- 4 x USB 2.0 ports
- CSI, DSI
- 5V/2.5A DC micro USB power input
Raspberry Pi 3 Model A+ specs (mostly the same as the Raspberry Pi 3 B+ but):
- 512MB RAM
- 1 x USB 2.0
- 65mm × 56.5mm (2.56in × 2.22in)
Raspberry Pi Zero specs:
- 1GHz single-core CPU
- 512MB RAM
- Mini HDMI
- Micro USB power
- Micro USB OTG port
- 40-pin header
- Composite video and reset headers
- 1.3v CSI camera connection
Raspberry Pi Zero W specs (same as Raspberry Pi Zero plus):
- 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Bluetooth Low Energy
ASUS Tinker Board specs:
- Rockchip RK3288 Cortex-A17 quad-core SoC
- ARM Mali-T764 GPU
- Up to 4K video support
- 2GB DDR3
- 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth 4.0
- 4 x USB 2.0 ports
- 15-pin MIPI CSI slot
- 40-pin GPIO header
- micro USB port for power
ASUS Tinker Board S (same as ASUS Tinker Board plus):
- 16GB eMMC
- HDMI-CEC
- Low-voltage input detection
- Plug-in detection, audio auto-switching
ASUS Tinker Board vs. Raspberry Pi: Hardware Options
The Raspberry Pi wins when it comes to variety. You'll find two Tinker Board variants, the vanilla Tinker Board and Tinker Board S. Compare that to the Raspberry Pi's whopping eight different versions. There's the Pi Zero and Zero W, Raspberry Pi 1 Model A+, Raspberry Pi 1 Model B+, Pi 2 Model B, Pi 3 Model B, Pi 3 Model B+, Pi 3 Model A+, and Raspberry Pi 4. This easily trounces the two Tinker Board iterations on the market.
Winner: Raspberry Pi
Head-to-head With the Raspberry Pi and ASUS Tinker Board: Connectivity
When it comes to connectivity options, the Raspberry Pi 3 B_ and ASUS Tinker Board are nearly identical. Both rock CSI slots, 40-pin GPIO headers, microSD card slots, and USB 2.0. Likewise, the Tinker Board and Raspberry Pi each feature Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. The Pi 4 rocks dual micro-HDMI However, the Tinker Board S adds a 16GB eMMC module. This lends vastly improved storage medium. Still, the Raspberry Pi 3 B+ boasts Bluetooth 4.2 and the Pi 4 packs Bluetooth 5.0 BLE, whereas the Tinker Board only has Bluetooth 4.0.
Winner: Raspberry Pi
Tinker Board Raspberry Pi Faceoff: Processing Power
While the Tinker Board churn out 4K videos with ease, the RasPi 4 can handle dual 4K monitors with its two micro-HDMI outputs. There's buttery-smooth streaming video and crystal clear local file playback. Benchmarks show the Tinker Board about for times as fast as the Raspberry Pi 3 B+, with the Pi 4 clocking in better benchmarks than the Tinker Board. The Rockchip Rk3328 Cortex-A17 GPU, Mali-T764 GPU combo means that ASUS Tinker Board is pretty powerful, but the Pi 4's Broadcom BCM2711 quad-core Cortex-A72 ARM v8 64-bit SoC trounces the ASUS. Sure, it's not going to replace your desktop or laptop, but it's nevertheless a beefy little dev board.
Winner: Raspberry Pi
Pi-Tinker Board Match-Up: Accessories
Because the ASUS Tinker Board comes in the same size as the Raspberry Pi 3 and 3 B+, virtually any Raspberry Pi case should work. The Pi 4 switches up its port layout, but there are still loads of cases and accessories like Pi HATs should all be compatible. You'll find a ton of awesome Tinker Board cases. Additionally, the two boards rock the same micro USB power supply. However, there are many more Raspberry Pi specific accessories, especially when factoring in the Pi 3 A+, Zero, and Zero W.
Winner: Raspberry Pi
OS Compatibility
When it comes to operating systems, the Raspberry Pi and ASUS Tinker Board are nearly even. The Pi runs a variety of OSes ranging from Raspbian to Ubuntu, Debian, Android, and retro gaming operating systems such as Lakka, Recalbox, and RetroPie. Tinker Board users may run TinkerOS, Ubuntu, Debian, Android, RetroPie, Lakka, Armbian, and more. For a home theatre PC, you may install LibreELEC, or FlintOS/Fyde OS for a Chromium OS PC. Essentially, there are plenty of distros for the Tinker Board and Raspberry Pi.
Winner: Tie
Support and Community
The ASUS Tinker Board definitely has its devotees. You'll find many forums and subreddits centered on Tinker Board tinkering. But the Raspberry Pi absolutely squashes the competition. With a sprawling community featuring thousands of users, the Pi by far brags the most resources including experts to follow on Twitter, books, tutorials, forums, and more. As such, dominates especially for beginner makers.
Winner: Raspberry Pi
Price
Starting as low as $5 USD, the Raspberry Pi ranks among the most affordable dev boards on the market. The flagship Raspberry Pi 3 B+ tops out at $35 USD. Then, the Raspberry Pi 4 comes in 2GB, 4GB, or 8GB RAM variants which range from $35 to $75. Compare that to the TinkerBoard which slides in at $60, and its fancier Tinker Board S at $80. For that price, you can pick up multiple Raspberry Pis.
Winner: Raspberry Pi
ASUS Tinker Board vs. Raspberry Pi: Which Single-Board Computer Should You Pick?
When selecting between the Raspberry Pi and ASUS Tinker Board, it's a tough choice. If you've got the money, I'd recommend buying both dev boards. I own a Tinker Board, a Pi 3 B+, and two Pi 4 boards, the 4GB and 8GB RAM models. Beginners should opt for a Raspberry Pi since there's more support, a larger community, and fantastic documentation for pretty much any project possible. Seasoned makers seeking an uber-powerful SBC should snag the ASUS Tinker Board. While similar, the two boards offer different pros and cons, from connectivity and price to processing power, which makes them almost equal. The Tinker Board is a fantastic Raspberry Pi competitor that you should definitely consider.
Which do you prefer, the ASUS Tinker Board or Raspberry Pi?












































