AI Smart Scale: Weigh, Recognize, and Track Food Nutrients Locally
The AI Smart Scale, developed by the makers behind the Engineering Dads YouTube channel, is a groundbreaking proof-of-concept project. This innovative device doesn’t just weigh food—it uses AI to identify the food item and provides a detailed breakdown of its macronutrients and calories.
Watch Ian talk about Tracking Calories and Macros using AI in this episode of The Electromaker Show
By combining the power of AI and IoT, this smart scale showcases how technology can seamlessly integrate into daily life, helping users make informed dietary decisions. With its unique approach and offline functionality, the AI Smart Scale stands as a promising prototype for the future of health-focused tech.
Key Features of the AI Smart Scale
Food Identification with AI: The scale employs a custom-trained TensorFlow Lite model to identify food items placed on its platform. The model runs locally on a Raspberry Pi 4, ensuring privacy and removing the need for cloud-based processing. This allows for quick and accurate recognition of foods, whether cooked or raw.
Weight Measurement: A precision scale measures the food’s weight in real time, enabling precise calculations of nutritional data. This weight, combined with the AI’s identification, provides an accurate macro breakdown for each food item.
Hardware Setup: The device features a dual Raspberry Pi setup: a Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W captures images of the food, while a Raspberry Pi 4 handles AI inference and database integration. This division of tasks ensures smooth and efficient operation.
Offline Functionality: All data processing is done locally, keeping user data private. Unlike many commercial devices, this proof-of-concept does not rely on cloud connectivity, making it both secure and independent.
How the AI Smart Scale Works
Process Overview: The system uses a camera mounted above the scale to capture real-time images of the food. These images are processed by the TensorFlow Lite model running on the Raspberry Pi 4, which identifies the food item. The scale measures the weight simultaneously, and these two data points are combined to generate an accurate nutritional profile.
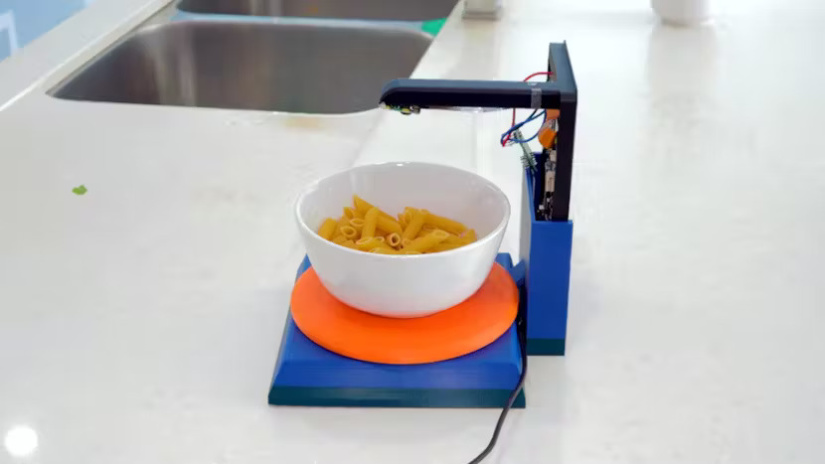

User Interaction: Once the food is identified and weighed, the smart scale displays the nutritional data on a connected screen. Users receive real-time feedback on calories, macronutrient composition, and other relevant dietary details, making the process seamless and user-friendly.
Database Integration: The AI Smart Scale relies on a preloaded database of food items and their macronutrient values. This database allows the system to calculate nutritional information accurately based on weight and food type, with potential for future expansion as new items are added.
Benefits and Potential Applications
Enhanced Dietary Awareness: By providing real-time calorie and macronutrient breakdowns, the AI Smart Scale helps users make informed dietary decisions. This tool is ideal for meal planning and tracking nutritional goals with minimal effort.
Privacy and Accessibility: With all processing done locally, the system ensures user data remains private. Unlike cloud-dependent devices, the AI Smart Scale functions independently, offering a secure and reliable solution for dietary tracking.
Future Commercial Potential: This proof-of-concept highlights the possibilities of AI in everyday devices. While the current model is a DIY project, a commercial version could integrate larger datasets and cloud support for broader food recognition capabilities, making it even more versatile.
Technical Challenges and Opportunities
Training the Model: One of the main challenges in developing the AI Smart Scale is training the TensorFlow Lite model to recognize a wide variety of food items. Expanding the database to include more foods, preparation methods, and variations would significantly enhance its accuracy and usability.
Hardware Optimization: Balancing performance and cost is another hurdle. While the dual Raspberry Pi setup ensures smooth operation, refining the hardware for a potential consumer-grade product would involve optimizing for affordability and compactness.
Open-Source Potential: The project’s open-source nature allows makers and developers to contribute to its growth. Enhancing the model, integrating additional features, or even adapting the scale for other use cases presents exciting opportunities for the maker community.
Did you enjoy this article?
Make sure you subscribe to The Electromaker Show for similar content and subscribe to our monthly newsletter!














































Leave your feedback...